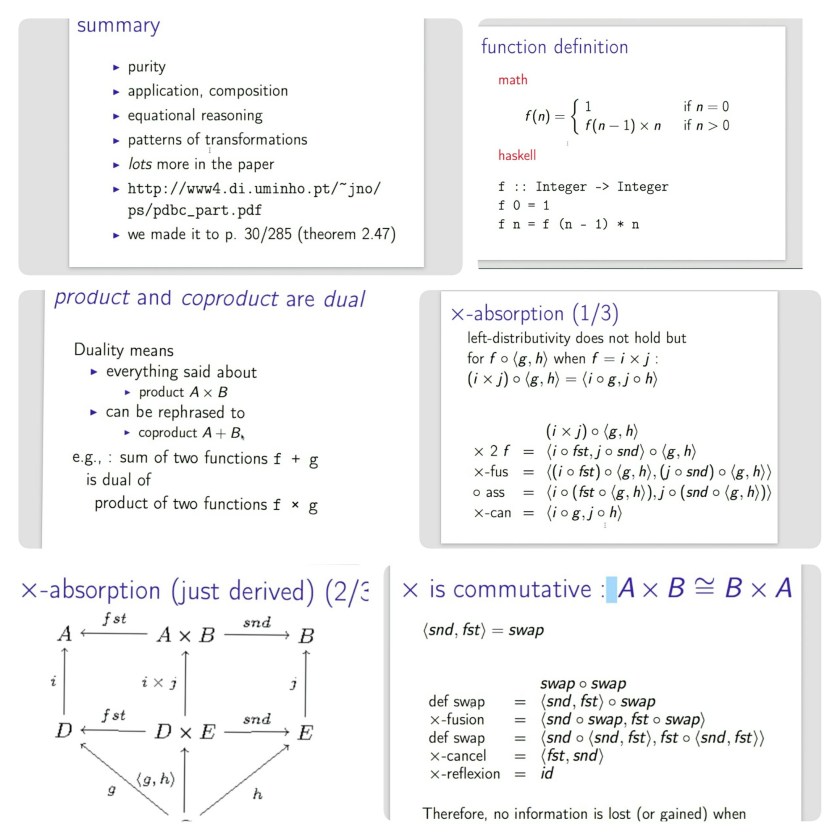
In 15 years, AI driven driverless car will change the transport/work/environment landscape… it is true not futuristic… behind AI is advanced math which teaches computer to learn without a fixed algorithm but by analysing BIG DATA patterns using Algebraic Topology !
世界趨勢,可作參考
矽谷预测AI後的10年大未來
現在因為人工智能(AI)的發展,配合更高速度的積體電路,科技正在加快速度的進展。據悉,在很短的5 -10年後,医療健保、自駕汽車、教育、服務業都將面臨被淘汰的危機。
1. Uber 是一家軟體公司,它沒有擁用汽車,卻能夠讓你「隨叫隨到」有汽車坐,現在,它已是全球最大的Taxi公司了。
2. Airbnb 也是一家軟體公司,它沒有擁有任何旅館,但它的軟體讓你能夠住進世界各地願出租的房間,現在,它已是全球最大的旅館業了。
3. 今年5月,Google的電腦打敗全球最厲害的南韓圍棋高手,因為它開發出有人工智能(AI)的電腦,使用能夠「自己學習」的軟體,所以它的AI能夠加速度的進步,達到比專家原先預期的、提前10年的成就。
4. 在美國,使用IBM 的Watson電腦軟體,你能夠在幾秒內,就有90%的準確性的法律顧問,比較起只有70% 準確性的人為律師,既便捷又便宜。
所以,你如果還有家人親友在讀大學的法律系,建議他們停學省錢,因為市場已大幅的縮減了,未來的世界,只需要現在10%的專業律師就夠了。
5. Watson 也已經能夠幫病人檢驗癌症,而且比醫生正確4 倍。
6. 臉書也有一套AI的軟體可以比人類更準確的鑒察(辨識)人臉,而且無所不在。
7. 到了2030年,AI的電腦會比世界上任何的專家學者還要聰明。
8. 2017年起,會自動駕駛的汽車就可以在公眾場所使用。
約在2020年,整個汽車工業就會遭遇到全面性的改變,你再不需要擁用汽車。
你可以用手機叫自動駕駛的車,來帶你到你想去的目的地。
9. 未來的世界,你再也不必擁有車,或花時間加油、停車、排隊去考駕照、交保險費,尤其是城市,將會很安靜,走路很安全,因為90%的汽車都不見了,以前的停車場,將會變成公園。
10. 現在,平均每10萬公里就有一次車禍,造成每年全球有約120萬人的死亡。
以後有AI電腦控制的自動駕駛汽車,平均每1000萬公里才有一次車禍,約減少一百萬人死亡。
因為保險費和需要保險的人極少,保險公司會面臨更多的倒閉風潮。
11. 大部份的傳統汽車公司會面臨倒閉。Tesla、 Apple、及 Google 的革命性軟體,將會用在每一部汽車上。
據悉,Volkswagen 和 Audi 的工程師非常擔心Tesla革命性的電池和人工智能軟體技術。
12. 房地產公司會遭遇極大的變化。
因為你可以在車程中工作,距離將不是選住房屋的主要條件之一。市民會選擇住在較遠、但是較空曠且環境優美的鄉村。
13. 電動汽車很安靜,會在2020變成主流。所以城市會很變成安靜,而且空氣乾淨。
14. 太陽能在過去30年也有快速的進展。 去年,全球太陽能的增產超過石油的增產。
預計,到2025年時,太陽能的價格(低廉)會使煤礦業大量的破產。
因為電費非常的便宜,淨化水及海水淡化的費用大減,人類將能解決人口增加的需水問題。
15. 健保:今年醫療設備商會供應如同「星球大戰」電影中的 Tricorder,讓你的手機做眼睛的掃瞄,呼吸氣體及血液的化學檢驗:用54個「生物指標」,就可檢驗出你是否有任何疾病的徵兆。
因為費用低,幾年後,全球人類都可以有世界級的疾病預防服務。
16. 立體列印(3D printing):預計10 年內,3D列印設備會由近20000美元減到400美元,而速度增加100倍快。
所有的「個人化」設計鞋子,將開始用這種設備生產,其他如大型的機場,其零件也能使用這種設備供應,至於人類太空船,也會使用這種設備。
17. 今年底,你的手機就會有3D掃瞄的功能,你可以測量你的腳送去做「個人化」鞋子。據悉,在中國,他們已經用這種設備製造了一棟6 層樓辦公室,預計到2027年時, 10% 的產品會用3D的列印設備製造。
18. 產業機會:
a. 工作:20年內,70-80% 的工作會消失,即使有很多新的工作機會,但是不足以彌補被智能機械所取代的原有工作。
b. 農業:將有 $100 機械人耕作,不必吃飯、不用住宅、及支付薪水,只要便宜的電池即可。在開發國家的農夫,將變成機械人的經理。溫室建築物可以有少量的水。
到2018年,肉可以從實驗室生產,不必養豬、雞或牛。30%用在畜牧的土地,會變成其他用途的土地。很多初創公司會供給高蛋白質的昆蟲當成食品。
c. 到2020年時 ,你的手機會從你的表情看出,與你說話的人是不是說「假話」? 是否騙人的? 政治人物(如總統候選人)若說假話,馬上會被當場揭發。
d. 數位時代的錢,將是Bitcoin ,是在智能電腦中的「數據」。
e. 教育:最便宜的智能手機在非州是$10美元一隻。
f. 到2020年時,全球70%的人類會有自己的手機,所以能夠上網接受世界級的教育,但大部份的老師會被智能電腦取代。所有的「小學生」都要會寫 Code,你如果不會,你就是像住在Amazon森林中的原住民,無法在社會上做什麼。你的國家,你的孩子準備好了嗎?
參考一下;這也是矽谷 VC, Innovators,Entrepreneurs … 談的資料。